Table of Contents
If it’s not your bone, what is the hardest substance in the human body? In a twist of biological artistry, the hardest substance in the body is the gleaming armor of your teeth – tooth enamel. This humble hero of your mouth is the ultimate guardian, and getting to know it might be the best thing you can do to keep your perfect smile.
Tooth enamel: The hardest substance in the body
You might be surprised that the hardest substance in the body is tooth enamel, not your bone. What is tooth enamel? Let’s find out what is tooth enamel and how it resides in your mouth.
What is tooth enamel?
Tooth enamel is the gleaming, protective outer layer that gives your teeth their pearly white appearance. But it’s far more than a pretty facade.
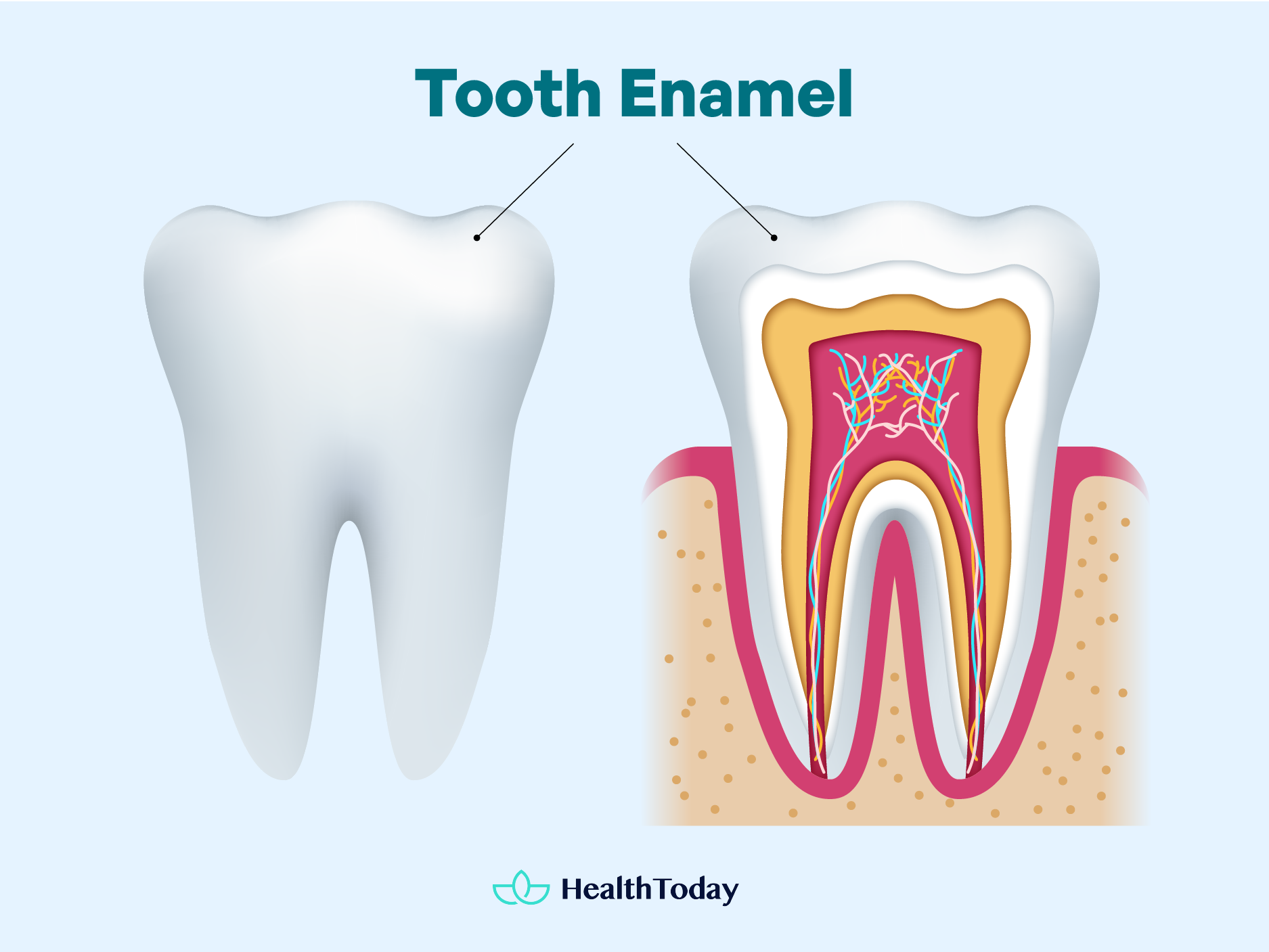
The composition of enamel is mostly mineral, primarily a tough substance known as hydroxyapatite. This crystalline structure is incredibly resilient and designed to shield your teeth from the daily wear and tear of life. It guards you against cavities, the sentinel against sensitivity, and ensures your teeth can handle the pressure of crushing and grinding (1).
During tooth development, enamel forms from the ameloblast cells inside the gums, creating a barrier that is, by adulthood, fully mineralized. However, unlike other parts of the body, enamel doesn’t regenerate (2).
Once there, it’s the final armor, with no natural reinforcements on the way. It’s no surprise that the hardest substance in the human body has to be incredibly strong; it’s not replenishing or self-healing.
How hard is tooth enamel?
To put it into perspective, the Mohs scale of hardness, which measures how well a substance can resist scratching, ranks enamel at about 5.
That’s on par with metals like steel, and just to illustrate, diamonds—a symbol of indestructibility—come in at a 10. But while enamel isn’t indestructible, it’s certainly the champion in our bodies, capable of withstanding incredible forces without so much as a scratch.
What can damage tooth enamel?
Your tooth enamel isn’t invincible. Acidic foods and drinks, like your morning grapefruit or that refreshing soda, can begin to dissolve enamel over time, a process known as erosion (3).
Furthermore, you might want to be more careful about your teeth if you’re following a vegetarian diet. A study suggests that a vegetarian diet might pose a greater risk of dental erosion, possibly due to the higher intake of acidic fruits and vegetables common in these diets (4).
Physical wear, such as from teeth grinding, can also strip enamel away, and bacteria from lingering food particles can produce acids that lead to cavities (5). Even over-brushing can wear down this hardy substance (6).
Can you rebuild tooth enamel?
Once enamel wears away, it’s gone for good—remineralization can fortify what’s there, but it can’t bring back what’s lost.
However, fluoride can help remineralize the enamel, acting almost like a healing salve that strengthens the molecular structure, making it more resistant to future attacks.
Scientific studies have shown that fluoride treatments can significantly boost this remineralization process. It encourages the absorption of minerals like calcium and phosphate from the saliva, integrating them back into the enamel (6, 7).
Ways to keep your tooth enamel healthy
Since your tooth enamel does not regenerate, it is important for you to keep it strong and protected. Here we give you some practical tips to help keep that enamel tough and healthy.
Diet
The journey to healthy enamel starts with what you eat. Calcium isn’t just for strong bones; it’s the cornerstone of healthy teeth.
Dairy products, leafy greens, and almonds are loaded with calcium and should be staples in your diet. But calcium’s sidekick, phosphate, is crucial and can be found in abundance in protein-rich foods like eggs, fish, and lean meat. Phosphates play a vital role in restoring minerals to teeth, which helps strengthen enamel (8).
Brushing
Your toothbrush is a tool, not a weapon. So when it comes to brushing, think of as massage, not scrub.
Soft bristles are the key to cleaning without causing abrasion to your enamel. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing once ensures you remove food particles and plaque that harbor harmful bacteria (9).
When you should see a dentist
If you’re noticing that your teeth seem to flinch at hot or cold temperatures or they’re not quite as white as they used to be, it’s wise to pay attention. These are subtle yet significant indicators of potential enamel erosion (10).
Besides these warning signs, regular dental checkups, ideally every six months, are an opportunity for early detection of enamel wear before it becomes a serious issue.
About 64% of adults over 18 in the US had a dental visit in 2022, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (11).
Other strong elements in your body
Your body is a marvel of nature’s engineering. It’s not just about the rock-hard tooth enamel but everything. Each strong element, from the keratin in your nails to the complex puzzle that is your bones, plays a critical role in our well-being.
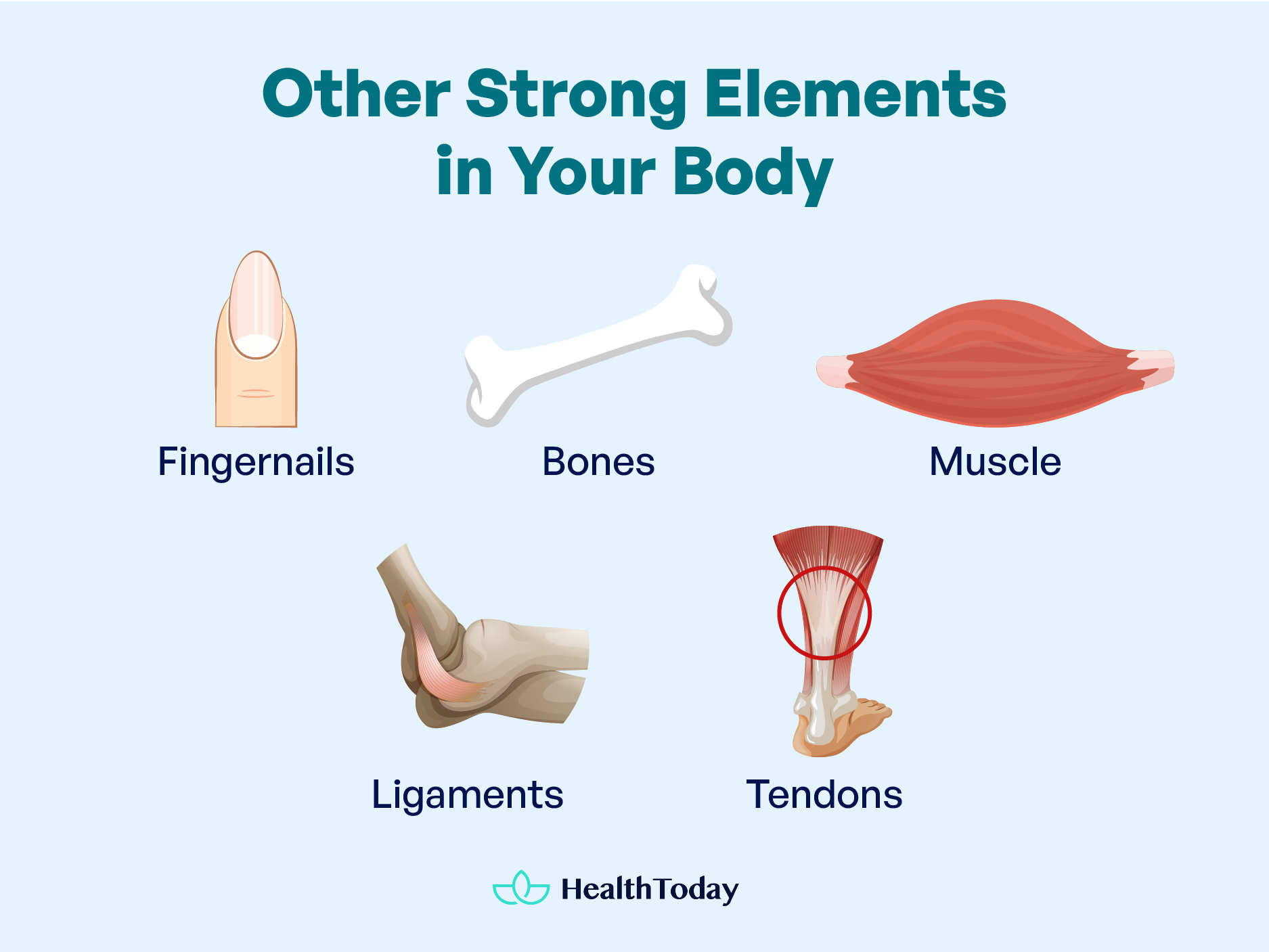
Fingernails
Fingernails serve as rigid protective plates for our delicate fingertips.
They are composed primarily of keratin, a protein that also forms the structure of our hair and skin’s outer layer. This protein gives nails strength and resilience, allowing them to withstand daily tasks like typing, scratching, or peeling (12).
To keep them robust, a diet rich in biotin, found in eggs and almonds, has been shown to improve their strength. Regular moisturizing also prevents brittleness, and protection from harsh chemicals maintains their integrity (13).
Bones
Though not the strongest, bones are strong and light enough to afford flexibility to be the framework of our body.
The secret to their strength lies in the composite nature of their makeup: a matrix of collagen fibers reinforced with calcium phosphate minerals. This combination allows bones to absorb shock and stresses, much like reinforced concrete (14).
In a way, bones are living sculptures that can heal themselves, continuously remodeling in response to the forces they encounter.
Weight-bearing exercises like walking and resistance training are proven ways to increase bone density and strength, along with a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D (15, 16).
Muscle
As engines of our body, muscles are composed of fibers that contract to produce movement. They possess a phenomenal ability to repair and strengthen themselves after injury or strain.
Protein is the building block of muscle, and consuming enough high-quality protein sources is essential for muscle repair and growth. Regular exercise is the stimulus that keeps muscles strong and resilient, as shown in countless studies linking physical activity with muscular health (17).
Ligaments
Ligaments are the tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect bones to other bones at joints. They’re made of many strong fibers all lined up together, which makes them very good at keeping joints stable when you move.
To maintain healthy ligaments, a balanced diet rich in collagen-boosting nutrients like vitamin C and regular exercise are beneficial (18, 19).
Tendons
While ligaments connect bone to other bones, tendons are the robust cords that attach muscles to bones, acting as the bridge that transmits the forces generated by muscles to create movement. Keeping tendons healthy involves regular stretching to maintain flexibility, proper technique during exercises to avoid overloading, and adequate rest to repair micro-injuries that can occur during intense physical activity (20).
Are teeth harder than diamonds?
Absolutely not! And don’t try the bite test to prove it! Diamonds are the hardest known natural material on Earth, ranking a solid ten on the Mohs hardness scale, whereas tooth enamel taps out at a respectable five. So while your teeth are tough enough to handle an overcooked steak, they’re not cut out for diamond-level challenges.
What is the 2nd hardest substance in our body?
If tooth enamel is the reigning champion of hardness in your body, then the silver medal goes to your bones, specifically the femur. Not as hard as enamel but still remarkably resilient, bones are constructed from a mix of collagen and infused with calcium phosphate, giving them strength and slight flexibility to not snap under pressure.
Which teeth are strongest?
Your molars are the Herculean heavy-lifters of your dental team. They come with a broader, flat surface designed for grinding down food, making them the strongest teeth in functionality. Plus, they have the added backup of being supported by multiple roots, giving them extra grip and power.
Are teeth a bone?
Teeth and bones share a family resemblance since they’re both white and contain calcium, but that’s where the similarities end. Bones can heal themselves; teeth cannot. Teeth are composed of enamel, dentin, pulp, and cementum, and while they’re in the skeletal ballpark, they don’t make the bone roster due to their different structure and inability to regenerate.
Are teeth naturally yellow?
That depends on your definition of “naturally.” If we peek underneath the enamel, there’s a core material called dentin, which has a naturally yellowish hue. So, a hint of yellow is perfectly normal. However, external factors like coffee guzzling and a fondness for red wine can add an extra layer of yellow patina, which might not be as natural as one would prefer.
Summary
So what is the hardest substance in the human body? Your tooth enamel. This mineral marvel stands guard against daily onslaughts, never to regenerate, so cherish the enamel you have. Keep those pearly whites healthy with a calcium-rich diet and gentle brushing with fluoride’s help, and don’t forget those important, regular dental visits. And while you’re at it, give a nod to the rest of your body’s tough team: bones, muscles, ligaments, and tendons, all working together to keep you strong.















Comments
0