Table of Contents
Pain in one of the arms or its joints is a common reason for seeking medical help. This type of pain can have various causes, ranging from skin conditions, joint issues, nerve problems, muscle strains, and blood vessel issues to heart or intra-abdominal problems.
The accompanying symptoms of arm pain can vary widely and include pain, itching, numbness, stiffness, swelling, or discomfort. These symptoms are often triggered by everyday activities like writing, using a cell phone, lifting heavy objects, or playing sports. However, in some cases, arm pain can be a sign of a serious condition, such as a heart attack.
Keep reading to learn more about the possible causes, symptoms, and various available treatments for this issue.
Understanding arm soreness
There are a wide range of causes why you might experience pain in one of your arms, from minor injuries like mild trauma to serious conditions such as heart attacks. Here are some of the possible causes:
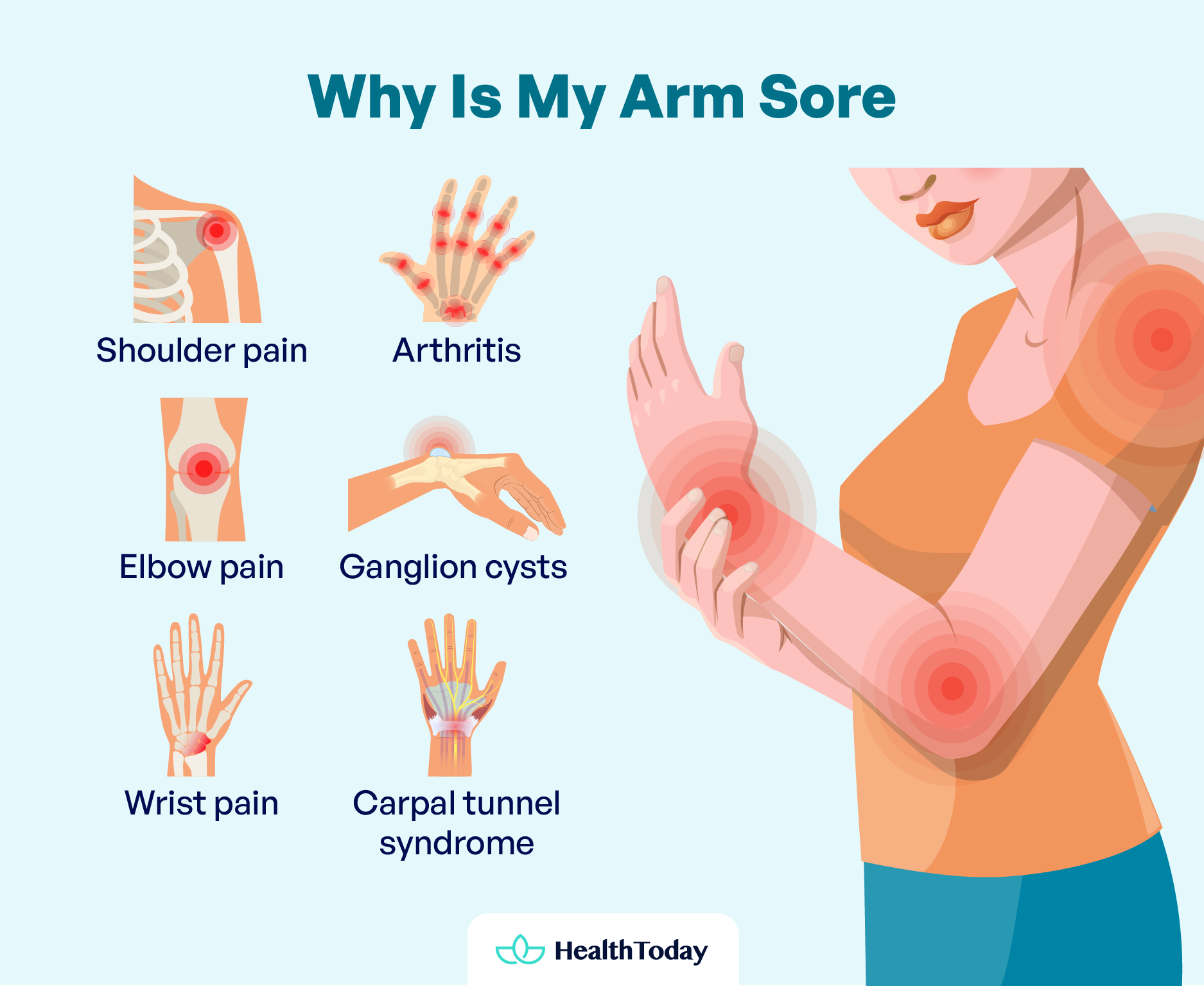
Shoulder pain
The shoulder joint is one of the most mobile joints in the human body. It allows us to perform a wide range of movements, such as lifting the arm, moving it forward and backward, and rotating it in different directions. This joint is made up of three main bones: the scapula (shoulder blade), the humerus (upper arm bone), and the clavicle (collarbone). To maintain mobility, it has several structures, such as the rotator cuff (group of muscles and tendons), the glenoid labrum (cartilaginous ring), the joint capsule (nourishes the joint), and ligaments.
Statistically, it is the joint that dislocates the most, especially in young patients and athletes (1).
The causes vary according to age. In young people, the most common causes are traumatic, due to sports or accidents, which generate acute pain. On the other hand, in older adults, the pains and injuries are subacute or chronic, and it is impossible to identify a single cause for them to occur.
The most frequent causes in older adults are (2, 3, 4):
- Bursitis of the shoulder: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion and protect the shoulder joints. Bursitis can cause pain and discomfort, especially during arm movements.
- Rotator cuff rupture: It is more frequent in older patients and usually does not result from a traumatic event but from a degenerative process of the tendons caused by many years of rotation and use. It presents as pain in the shoulder during daily activities or sports or discomfort when taking the hand to the back.
- Supraspinatus calcifying tendinitis: It is one of the most frequent causes of shoulder pain. It consists of calcific deposits in the tendons of the cuff, especially in the supraspinatus tendon. It is more common in middle age, and it is more frequent in women. It is characterized by a pain of great intensity that even interrupts the night’s rest. This pain usually decreases in intensity during the day.
- Tendinitis of the rotator cuff: It can be triggered by overexertion, although sometimes its presentation does not have the antecedent of efforts or traumatism. It presents as pain especially when performing certain shoulder movements. The most painful movements are elevation and rotation, bringing the shoulder to the back.
In general, shoulder pathologies are diagnosed by a correct physical examination and a study of images, including simple radiography, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance. Treatment depends on the cause of the pain and ranges from limiting shoulder overload to anti-inflammatory drugs to surgery in some instances.
If shoulder pain is severe and persistent or affects the ability to perform daily activities, it is essential to seek medical attention. An accurate diagnosis is vital to receiving proper treatment and avoiding long-term complications.

Elbow pain
The elbow is the central joint between the arm and the forearm. It allows us to bend and straighten the arm and turn it inward and outward. The structures that meet are the bones of the humerus (upper arm), ulna, and radius (forearm). In addition, the joint is stabilized by muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
The causes of elbow pain are usually inflammation or overstretching of soft tissues, such as tendons or ligaments. In some cases, the pain may be the result of chronic pathologies, such as:
- Osteoarthritis: This condition is characterized by bone degeneration due to the loss of calcium and phosphate deposits in the bone. Arthrosis can affect the elbow joints, causing pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: This type of arthritis occurs when autoantibodies cause inflammation and destruction of the joints. Other types of arthritis include gouty arthritis, which occurs when there is too much uric acid in the blood, and psoriatic arthritis, which often comes with skin conditions and is also due to an overactive immune system. These conditions can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the elbow, in addition to other systemic symptoms.
Most cases of elbow pain will get better on their own or with simple self-help treatments.
For home treatment of an arm injury, you can try the following measures:
- Cold therapy: Apply ice packs to the affected area several times a day for no more than 15 minutes at a time. This can help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Over-the-counter medications: Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen, can help relieve pain after an injury. However, if you have any pre-existing medical conditions, it is important to check with your doctor before taking any medication.
- Immobilization: In the event of a moderate or severe injury that causes pain, it is advisable to immobilize the arm to allow it to recover properly. This can help prevent further damage and facilitate recovery.
- Rehabilitation exercises: After the acute period of the injury, you can begin gentle rehabilitation exercises to restore the range of motion and strengthen the affected muscles. It is important to perform these exercises under the supervision of a medical professional to avoid further injury.




Wrist pain
Wrist pain can vary depending on the cause. For example, osteoarthritis pain is described as a pain similar to a dull ache without much intensity, while carpal tunnel syndrome causes a tingling sensation, especially at night.
Cause
Damage to any part of the wrist can cause pain and affect the ability to use the wrist and hand.
Injuries
- Trauma. Wrist injuries occur when a person falls forward or backward on an outstretched hand. This can cause sprains, strains, and even fractures. We suspect the latter when there is a deformity or prolonged pain over time.
- Repetitive strain. Any activity that involves repetitive wrist motion can generate wrist pain. Excessive cell phone use has been shown to generate a disease called De Quervain tenosynovitis, characterized as tendinitis that causes pain at the base of the thumb that increases with movement (5).
Arthritis
- Arthrosis. This type of arthritis occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones deteriorates over time. Osteoarthritis in the wrist is rare and usually occurs only in people who have injured their wrist in the past.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. A disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues. It commonly affects the wrist, and If one wrist is affected, the other is usually affected as well.
Other diseases
- Carpal tunnel syndrome. It occurs when there is increased pressure on the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel, a passageway on the palm side of the wrist. The typical symptom is tingling of varying intensity in the fingers, especially the thumb and index finger, weakness of the hand in gripping, and occasionally swelling. Symptoms are usually worse at night.
- Ganglion cysts. In most cases, these soft tissue cysts occur on the side of the wrist opposite the palm. Ganglion cysts can be painful, and the pain may worsen or improve with activity.
Not all wrist pain requires medical attention. Icing, rest, and over-the-counter pain relievers usually work for minor sprains and strains. But if pain and swelling last more than a few days or worsen, see your doctor. Delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to poor healing, reduced range of motion, and long-term disability.
Muscle pain in arm or heart-related issues?
Arm pain is often associated with a heart attack. Although a heart attack can cause arm pain, it is important to remember certain key points to differentiate it from muscle pain.
Heart-related arm pain
The typical presentation of acute myocardial infarction (i.e., Heart Attack) is characterized by:
- Very intense chest pain, usually described as stabbing, oppressive, burning, or discomfort. The pain may spread to areas such as the inside of the left arm, shoulder, jaw, or back.
- It is often associated with other symptoms such as shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or fainting.
- It may be triggered by emotional stress or physical activity, but can also occur at rest.
It is important to clarify that it usually occurs in patients with risk factors such as obesity, hypertension, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy lifestyle, and a history of arterial disease.
Muscular arm pain
- It is usually localized and can be reproduced by touching or moving the affected area.
- It can be caused by overexertion, strenuous exercise, or muscle tension.
- Muscle pain can vary in intensity and is usually felt as a dull, aching, or throbbing. It is usually confined to the affected area and does not radiate to other parts of the body.
- Muscle pain usually improves with rest, heat, massage, or over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications.
In the United States, someone has a heart attack every 40 seconds (6), so it is recommended that if you have the symptoms described above, see a doctor immediately.
How to reduce muscle pain in the arm?
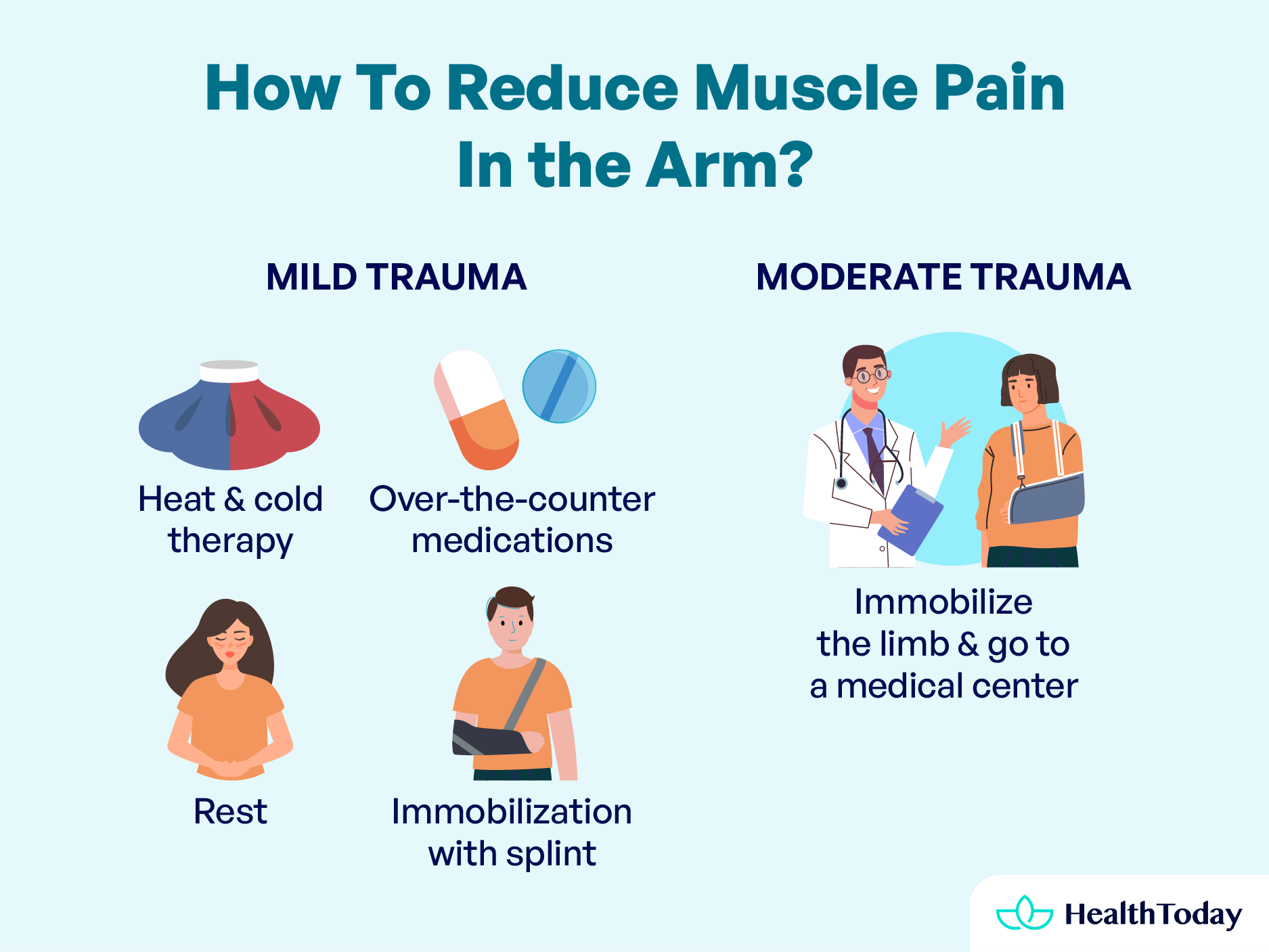

Most arm pains are acute and caused by sudden injuries and usually calm down with home treatments.
It is recommended that when faced with arm pain, first identify whether it was due to trauma, repetitive movements, overexertion, or if it appears spontaneously. If it was due to a mild trauma, and you can move the limb with a low pain level, it is recommended:
- Heat and cold therapy: Apply warm compresses or ice packs wrapped in towels to the painful and inflamed area for 15 minutes several times a day.
- Rest: In the acute period of trauma, it is recommended not to make movements as they may exacerbate the injury.
- Immobilization with splint: In the first instance, until more serious causes are ruled out, immobilization of the affected limb is recommended.
- Over-the-counter medications: Medications such as paracetamol/acetaminophen and NSAIDs such as ibuprofen can help relieve your pain in the acute period.
If you have moderate trauma, you cannot move the limb, and the pain is intense, it is recommended to immobilize the limb and go to a medical center.
When to see a doctor
It is important to consider several factors when determining when to see a doctor for arm pain. While some arm pain may resolve on its own with rest and self-care, persistent or severe pain may indicate a more serious underlying problem. So we recommend consulting your doctor when:
- Sudden or severe pain: If you experience sudden, intense, or severe arm pain with no obvious cause, it is wise to seek medical attention immediately, especially if the pain persists or worsens over time.
- Injury: If your arm pain is the result of an injury, such as a fall, blow, or repetitive strain injury, and does not improve with rest and home remedies, it is crucial to have it evaluated by a physician to rule out fractures, dislocations, or other injuries.
- Pain accompanied by other symptoms: If your arm pain is accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, redness, warmth, numbness, fever, or weakness, it could indicate an underlying medical condition such as a joint infection.
- Persistent pain: If you have had persistent or recurring arm pain that does not improve with rest, ice, over-the-counter pain medications, or other self-care measures, then you should see a medical expert.
- History of heart disease or risk factors: If you have a history of heart disease, or risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease and you experience arm pain along with chest pain, shortness of breath, or other symptoms suggestive of a heart problem, seek medical attention immediately, as it could be a sign of a heart attack.
In general, if you are in doubt about the cause of your arm pain or if you are concerned about its severity or persistence, it is best to err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.




What does it mean when your whole arm hurts?
Pain throughout the arm may be due to muscle strain, nerve compression, or underlying medical conditions such as arthritis or circulatory problems.
What can I take for arm pain?
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may help relieve arm pain. Topical Anti-inflammatory may also be helpful.
Why are my arms sore after a long run?
Soreness in the arms after a long run could result from muscle fatigue or overuse. To improve arm endurance and reduce soreness, ensure proper warm-up and cooldown routines, stay hydrated, and consider incorporating strength training exercises.
Can muscle pain in the arm come and go?
Muscle pain in the arm can come and go, particularly if it’s related to factors such as overuse, muscle strain, or repetitive motions.
When should I worry about bicep pain?
Suppose you experience severe pain in the biceps during exertion, accompanied by a popping sound at the time of injury and an obvious deformity in the affected area. In that case, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. These symptoms indicate a possible rupture of the long portion of the biceps.
Summary
Arm pain can have multiple causes, from minor injuries to serious cardiac problems, such as acute myocardial infarction. The first step when faced with arm pain is to identify its cause since it may be due to overexertion, trauma, or no apparent cause. In addition, it is essential to observe the accompanying symptoms, such as swelling, tingling, difficulty moving the arm, or fever, to rule out serious pathologies.
Acute myocardial infarction is one of the most serious pathologies that should be ruled out, especially if there are risk factors or symptoms of chest pain. At the slightest suspicion of this condition, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosis can be based on clinical evaluation, although specific cases like shoulder or wrist problems may require imaging tests such as ultrasound, X-ray, or MRI.
In addition, it is important to consult a physician if you experience sudden or severe pain, if the pain persists after an injury, or if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, weakness, or fever.
















Comments
0